ACCP Staff
ACCP and YourCause from Blackbaud recently surveyed the corporate social impact field to better understand the trends impacting corporate social responsibility (CSR) and Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) professionals. The survey was conducted in April of 2023, and garnered responses from 149 companies representing more than $1 billion in community investment.
The survey results show a profession experiencing continued instability and change which may hinder its ability to successfully maintain momentum toward the goals of positively impacting society and meeting key stakeholder expectations.
2023 Key Findings
The ever-increasing demands on and responsibilities of corporate social impact teams are creating adverse consequences.
Most survey respondents (86%) indicated their team had more responsibilities in the past year, a 6% increase from one year ago when an already high 80% said that demands on their team had increased. Further, 58% indicated they need more resources to meet these expectations.
This ongoing trend comes with real consequences. Impacts cited included longer hours (61%), burnout (50%), fear of not meeting expectations (46%), and mental health concerns (19%).
Company executives, sometimes not as well-versed in the specifics of CSR and ESG work, must understand these consequences, particularly in a tight labor market.
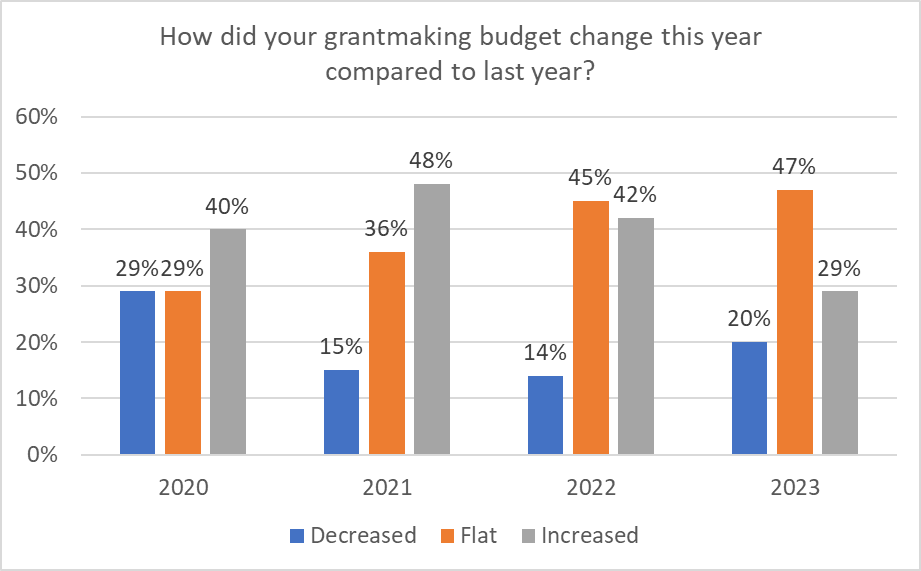
Increases in grantmaking budgets slowed for the first time since before the pandemic, and cuts inched higher.
In 2023, the lowest percentage of companies increased their grantmaking budget since this study began in 2020, declining from a high of 47% in 2021 to a low of 29% this year. This trend is likely a reflection of the uncertain economy.
Corporate structures and terminology are changing as the relevance of corporate social impact grows and the work evolves.
When asked what name companies use for this work, no one term received a majority of responses. The most frequently used title for the work was corporate social responsibility (21%) or names leading with the word “community,” e.g., community impact, community relations, community affairs, or community engagement, which collectively comprised 23%.
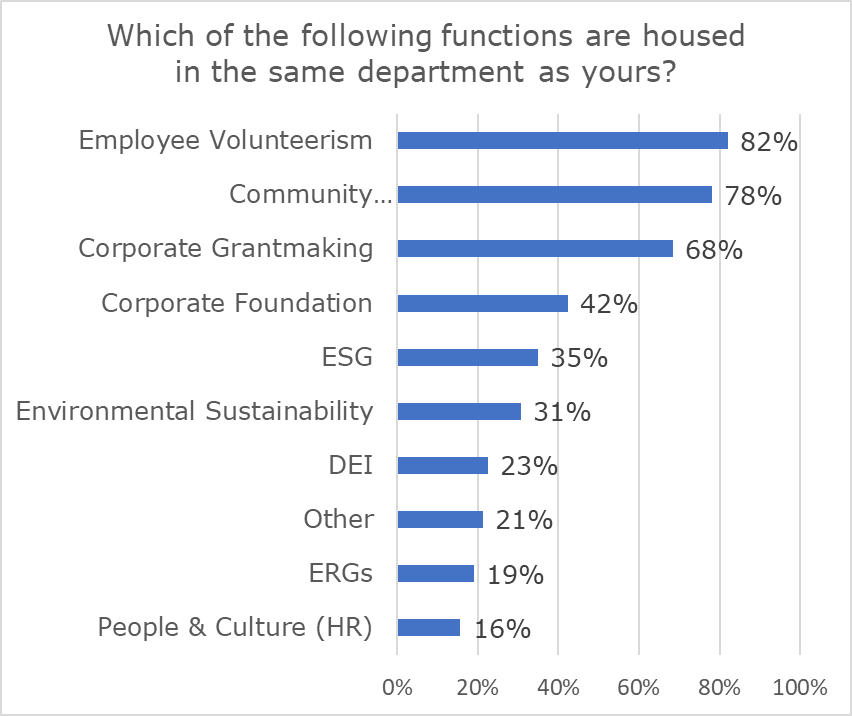
The survey results also revealed that the structure and functions of departments are varied. The most frequently cited combination of functions housed in the same department included employee volunteerism, community relations, and corporate grantmaking.
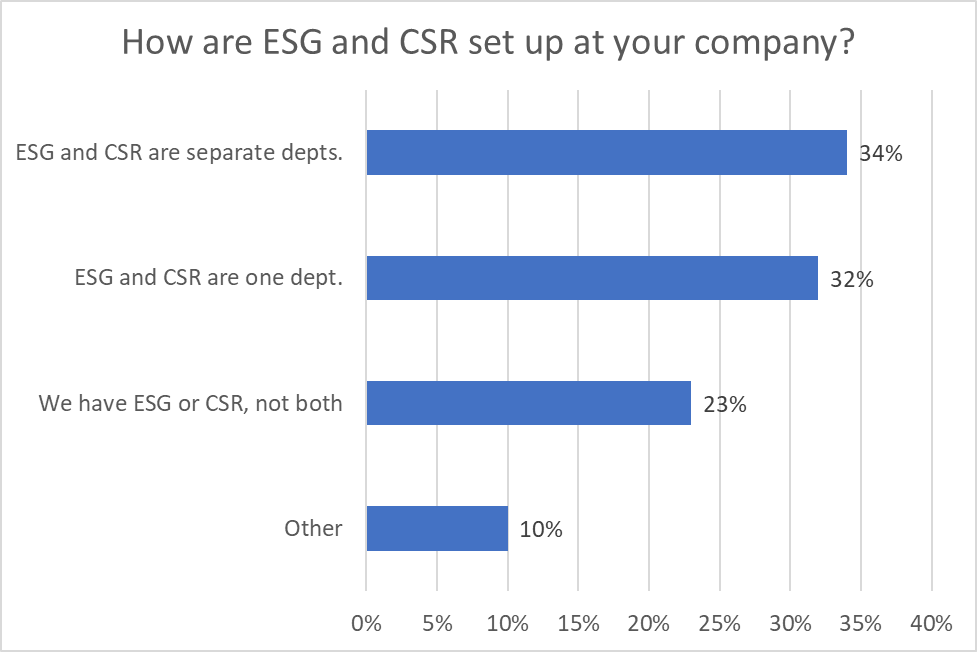
The structural relationship between CSR and ESG is also varied. One-third (33%) of respondents indicated that the CSR and ESG functions reside within one department, and one-third (34%) indicated that their companies’ ESG and CSR functions are housed in separate departments. This variety in structure across companies makes benchmarking and measurement challenging.
The top three issue areas companies are prioritizing are environmental sustainability, education, and food insecurity.
This year, the top three priority social issues are environmental sustainability (56%), K-12 education (53%), and food insecurity (49%).
Of note, Racial justice/Equity was indicated as a priority issue by 44% of respondents as compared to 50% last year. (In 2021, racial equity was identified as a “new priority” by 64% of respondents).
Participation in employee volunteerism is increasing and continues to adapt to the changing workplace.
Most (61%) survey respondents reported that participation in employee volunteer activities has increased, a welcome sign compared to the decline in recent years. The focused effort to increase participation in volunteer activities supports the belief that employee volunteerism is an effective strategy for increasing engagement and tangibly aligning corporate values with those of employees.
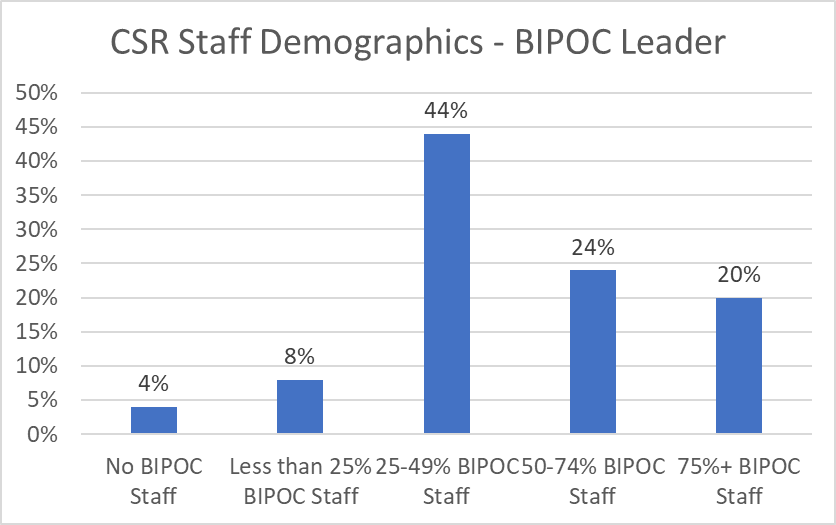
White women continue to dominate the corporate social impact profession. However, teams are significantly more diverse if the team leader is a person of color.
87% of survey respondents indicated they worked on a team where fewer than 50% of teammates were people of color.
However, the data suggests that there may be some progress in the overall diversity of CSR teams over the past two years, as the percentage of companies that reported less than 25% of their teammates were people of color declined by 9% from 2021 (35%) to 2023 (26%).
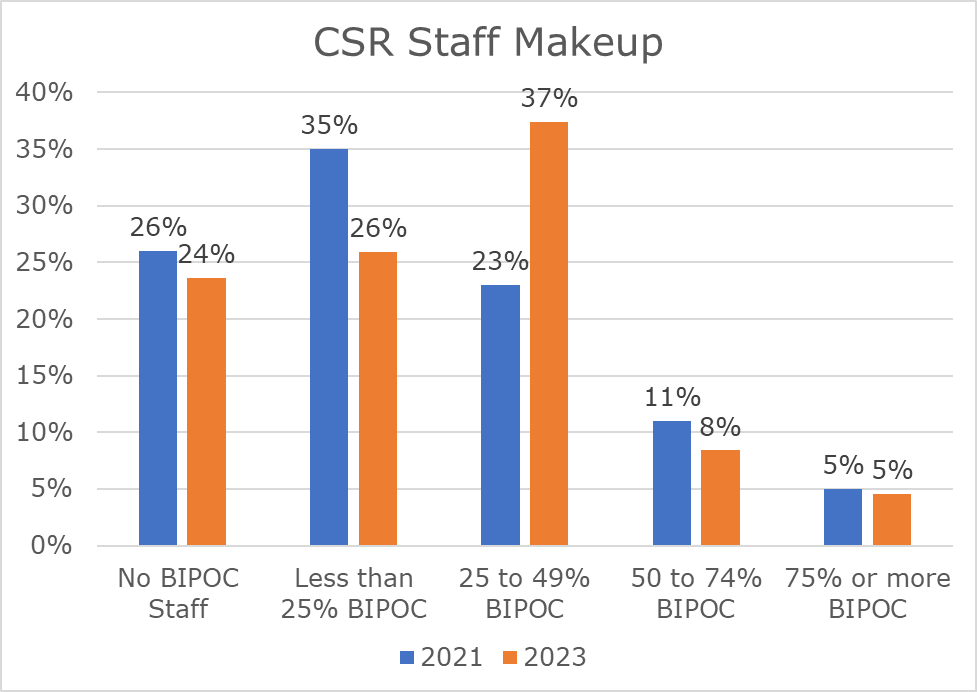
An important finding of this year’s survey is that corporate social impact teams are significantly more diverse when the team leader is a person of color. 88% of survey respondents who indicated their team lead was a person of color worked on a team with more than 25% diversity.